
Drop Shipping
What Is Drop Shipping?
Drop shipping is a retail fulfillment model where the supplier ships products directly to the customer on behalf of the retailer.
The retailer does not hold or manage physical inventory but acts as the storefront and sales channel.
In essence, drop shipping allows brands and retailers to sell products without owning stock, while fulfillment and shipping are handled by the supplier or manufacturer.
Why Drop Shipping Matters for Brands
For retail and fashion brands, drop shipping enables assortment expansion and faster market entry with lower inventory risk.
However, it requires strong operational coordination to maintain service quality.
Key benefits:
No upfront inventory investment
Faster assortment expansion across categories
Reduced warehousing and storage costs
Key challenges:
Limited control over shipping speed and packaging
Dependency on supplier SLAs and accuracy
Complex returns and customer service coordination
Examples of Drop Shipping in Action
Imagine an online fashion marketplace onboarding new brands.
With drop shipping, they can:
List products without receiving physical inventory
Route orders directly to suppliers for fulfillment
Offer a broader assortment with minimal risk
Scale quickly across categories and regions
Drop shipping is commonly used for long-tail products, extended sizes, or niche categories.
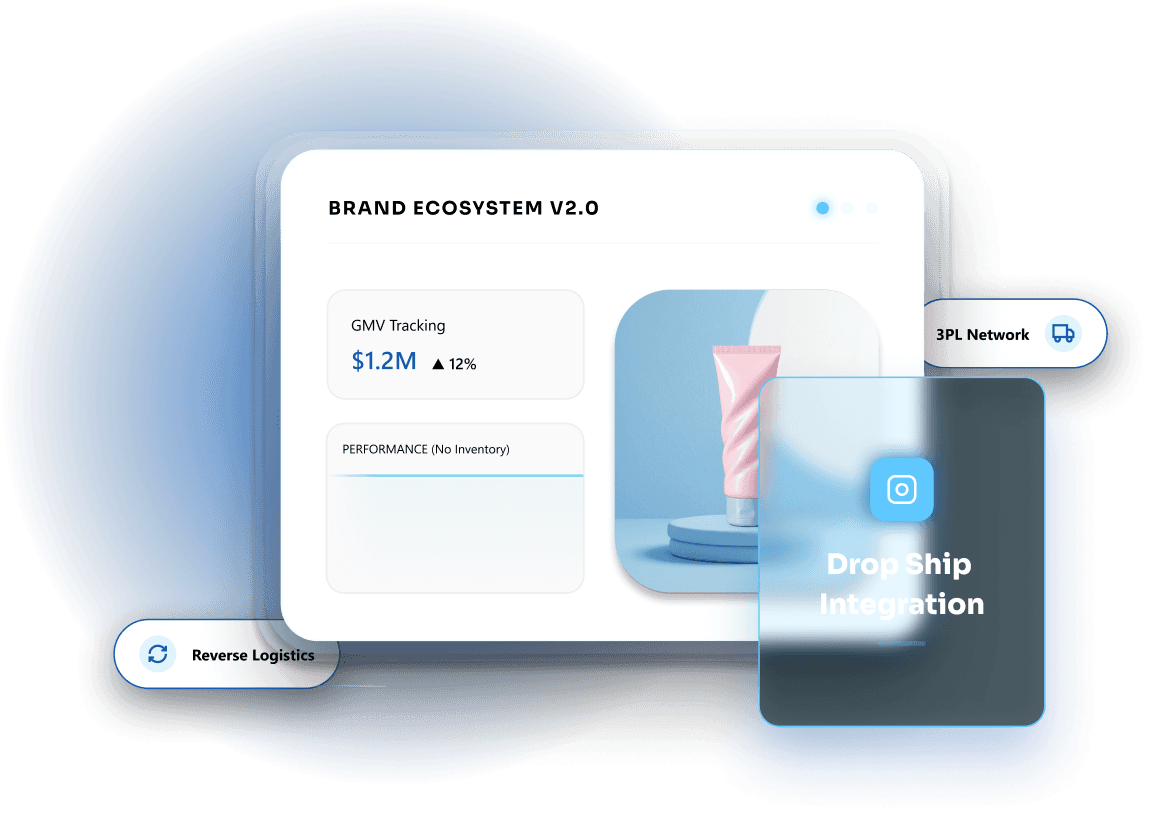
How Drop Shipping Fits into the Ecosystem
Drop shipping often connects with:
Third-Party Logistics (3PL): To support fulfillment and delivery coordination
Reverse Logistics: To manage returns shipped back to suppliers
GMV Tracking: To measure performance without inventory ownership
Together, these systems help brands operate drop shipping models with clearer visibility, accountability, and control.
Related Terms
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Reverse Logistics
Gross Merchandise Value (GMV)
Fulfillment SLAs

